
What is Toolchain?
Toolchain이란 말 그대로 Cross Develepment를 위한 도구들의 집합이다.
 Ref: Linux Foundation 2020 Conference
Ref: Linux Foundation 2020 Conference
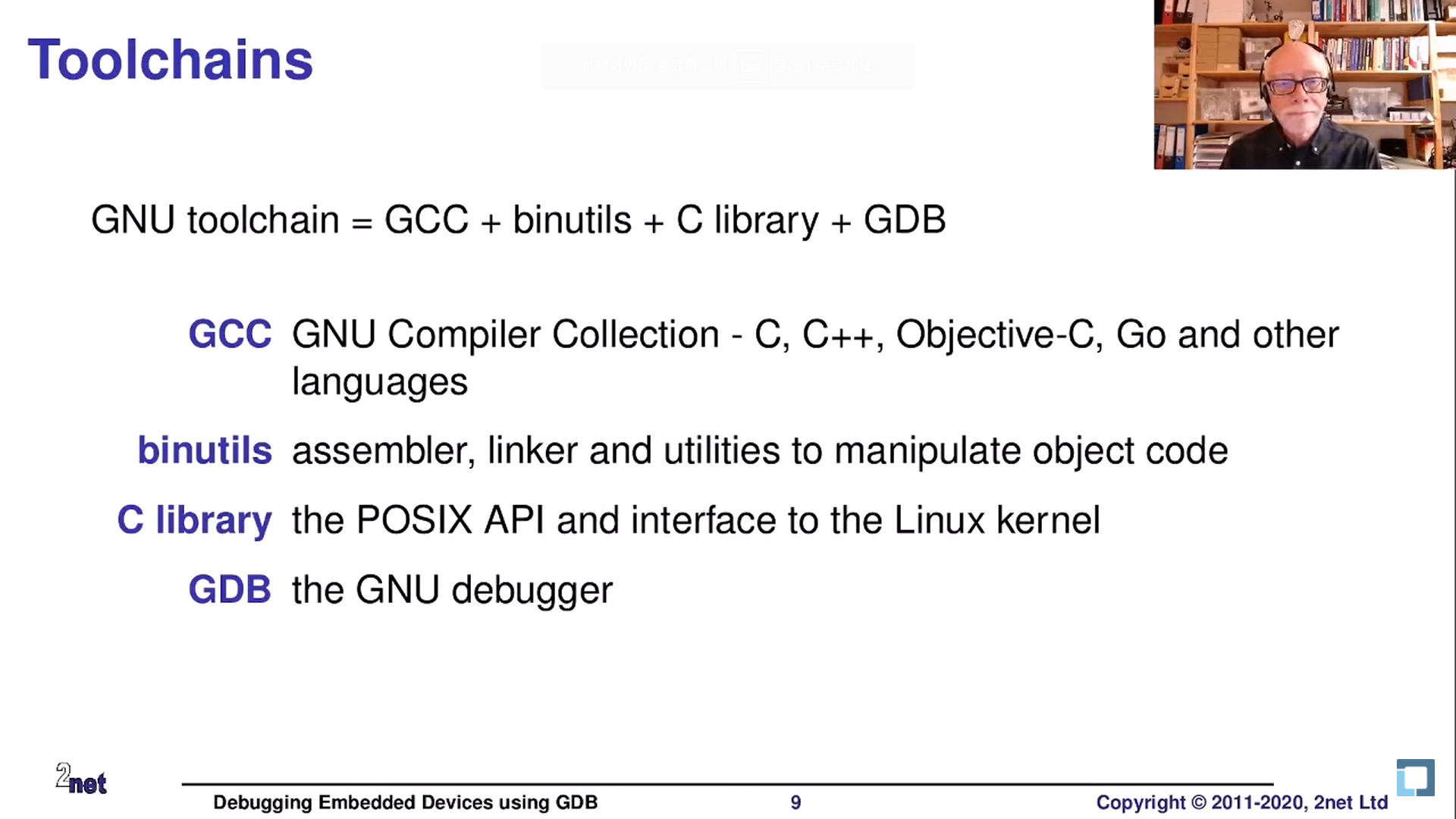
위 그림처럼 GNU Toolchain은 크게 컴파일러, binutils, C 라이브러리, GDB 디버거로 나뉘어진다.
- 컴파일러 : 호스트 개발환경에서 타겟의 아키텍쳐로 컴파일하기 위한 도구이고
- binutils : 컴파일한 Object 들을 컨트롤하기 위한 어셈블러, 링커 등
- C 라이브러리 : POSIX 및 리눅스 커널 인터페이스
- GDB : GNU 디버거
Getting a toolchain
 Ref: Linux Foundation 2020 Conference
Ref: Linux Foundation 2020 Conference
위 그림처럼 Toolchain은 보통은 칩 제조사에서 제공을 한다. 혹은 Linaro 같은 유명한 Third Party를 통해 다운로드 할수도 있고, Yocto Project같은 빌드 시스템을 사용하면 편하게 얻을 수 있다.
Toolchain prefix
 Ref: Linux Foundation 2020 Conference
Ref: Linux Foundation 2020 Conference
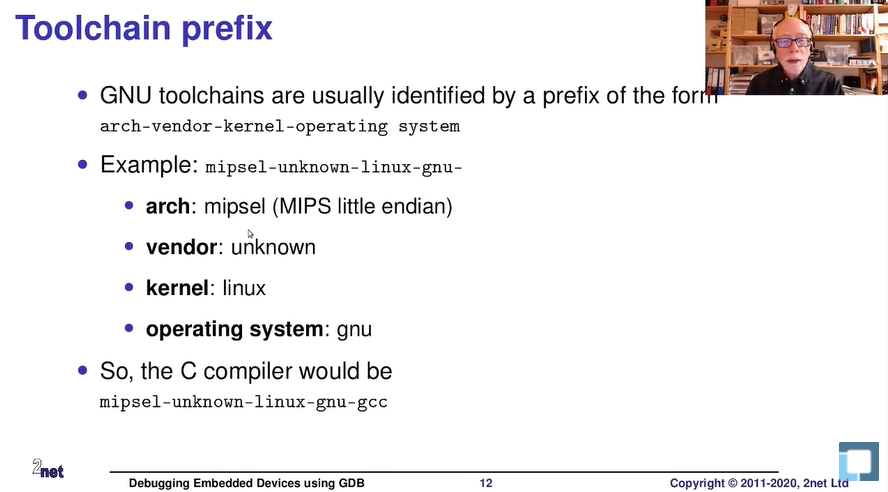
위 그림을 통해 Toolchain의 작명 룰을 살펴보자.
”-“ 를 통해 구분하며 순서대로 “아키텍쳐-제공사-커널명-OS명” 으로 지어진다.
Toolchain prefix for ARM toolchain
 Ref: Linux Foundation 2020 Conference
Ref: Linux Foundation 2020 Conference
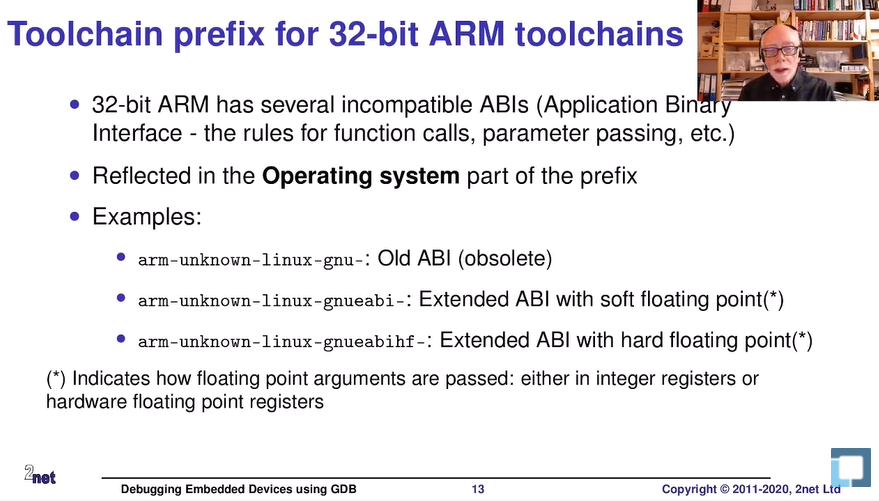
Toolchain 네이밍 마지막은 OS라고 위에서 언급했다. 여기에 추가적으로 ABI(Application Binary Interface)가 더 붙게된다.
이는 타겟 OS가 어플리케이션간 어떠한 인터페이스로 Binary 데이터를 주고 받는지에 대한 규칙을 말해준다.
- 데이터 타입과 정렬 방법
- 함수 호출 시 인수 및 결과에 대해 레지스터 교환 방법
- 시스템 콜 호출 방법
- 프로그램 코드의 시작과 데이터에 대한 초기화 방법
- 파일 교환 방법(ELF 등)
위 그림에서 처럼 오래된(Old or obsolete) ABI는 OS뒤에 덫붙이는 것을 생략한다. 이는 32bit의 ARM 아키텍쳐를 지원하던 시절에 이용되었다.
EABI(Embedded ABI) 부터는 임베디드 환경에서 64bit 아키텍쳐를 지원하기 위해 만들어졌다. (ARM, PowerPC, MIPS 등)
eabi도 그냥 사용하면 softfloat이고 뒤에 hf를 붙여 eabihf로 사용하면 hardfloat이다. 그 차이점은 아래와 같다.
- softfloat
- FP instruction을 만들지 않고 GCC가 컴파일타임에 라이브러리에서 함수로 준비
- hardfloat
- FP instruction을 에뮬레이션한다.
A CPU like the ARM can do calculations. In most programs most of these calculations are of the “whole numbers” (integer) type, as these are very simple to do electronically. Some programs also do “floating point” calculations, and these programs also are expected to work on CPU’s that do not have the hardware to do floating point calculations. In such cases these calculations are automatically routed, by the operating system, to a library of calculation routines that do these calculations using integer calculus. For example a simple division like 2/3 is done with hundreds of integer calculations. This is called “software floating point calculus”, or short “soft float” But the ARM chip has a CPU that can also do floating point calculations directly in hardware! This happens very much faster, as a floating point calculation in hardware is almost as fast as a integer calculation. hardware floating point calculus is shortened to “hard float”. In the past the R-PI’s operating systems did not “know” the R-PI’s CPU could do floating point calculus, so all floating point calculations were done using the software library. With the latest OS’s they became “aware” of the hard float capability of the PI and began using it, which means a very big speed increase for programs using a lot of floating point calculations.
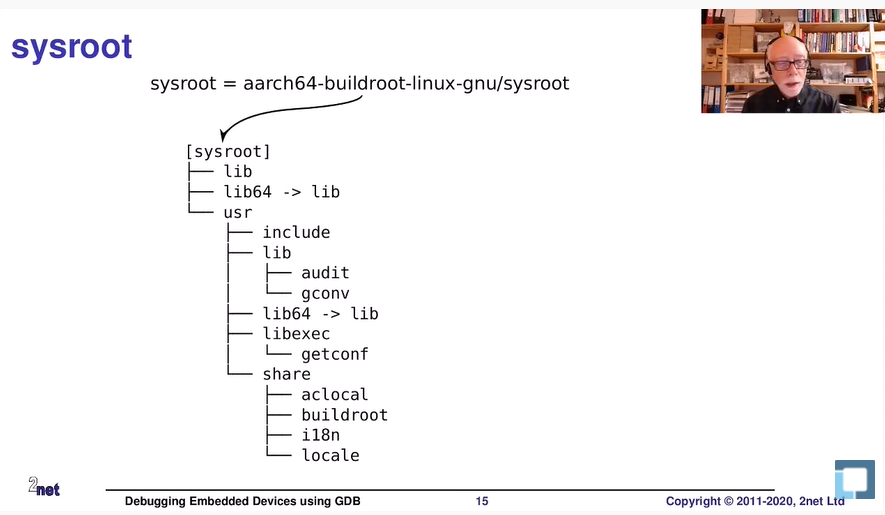
Toolchain sysroot
 Ref: Linux Foundation 2020 Conference
Ref: Linux Foundation 2020 Conference
sysroot란 실제 타겟환경에서 가지게 되는 rootfs를 의미한다.
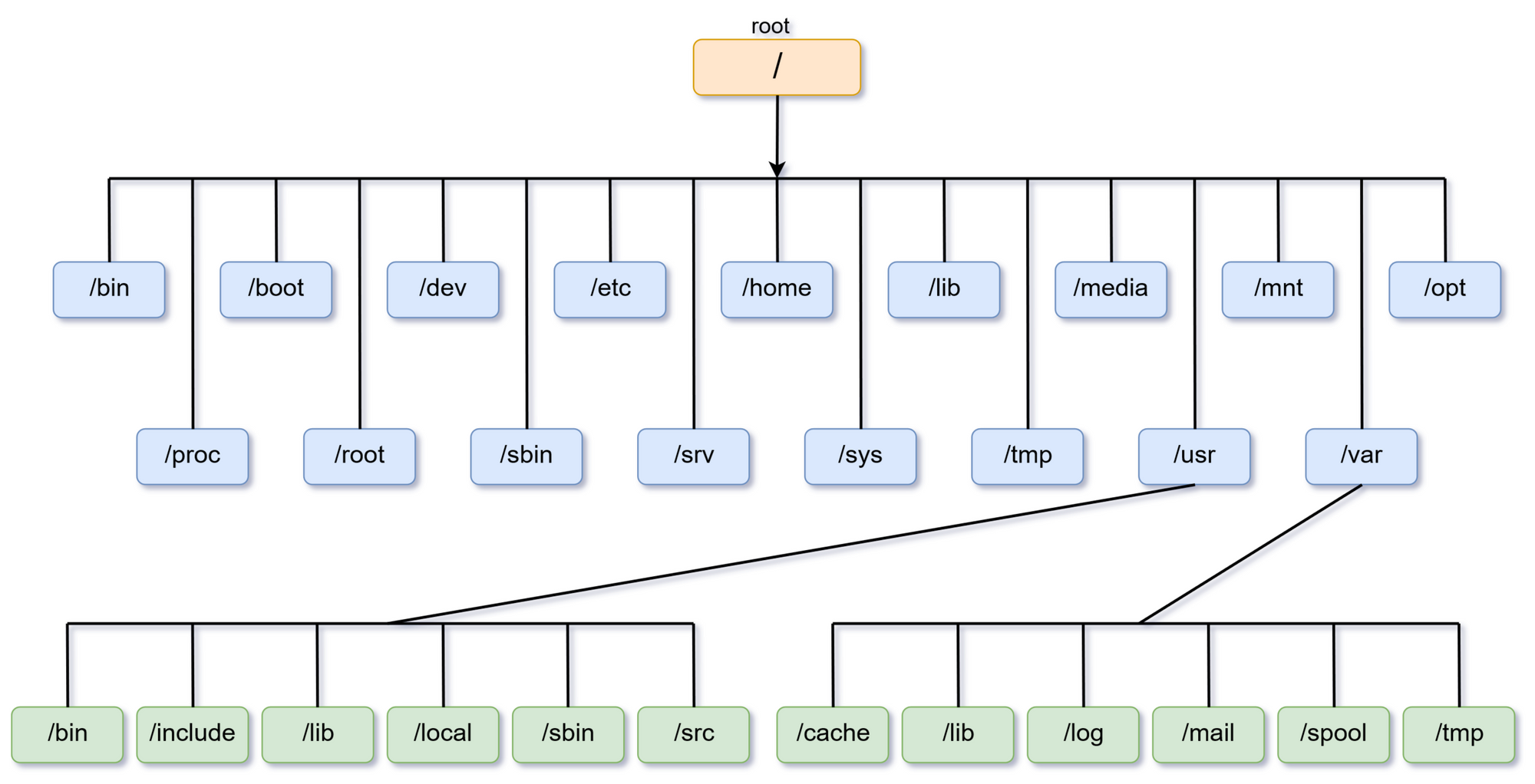 Linux rootfs
Linux rootfs
The root file system (named rootfs in our sample error message) is the most basic component of Linux. A root file system contains everything needed to support a full Linux system. It contains all the applications, configurations, devices, data, and more. Without the root file system, your Linux system cannot run.
 Ref: Linux Foundation 2020 Conference
Ref: Linux Foundation 2020 Conference
그 타겟환경 안에 있는 모든 것이 다 필요하지는 않고, 그 중에 Cross-development를 위한 일부분만 있으면 된다.
예를들면 라이브러리와 헤더파일 등이 있다.
What Toolchain contains
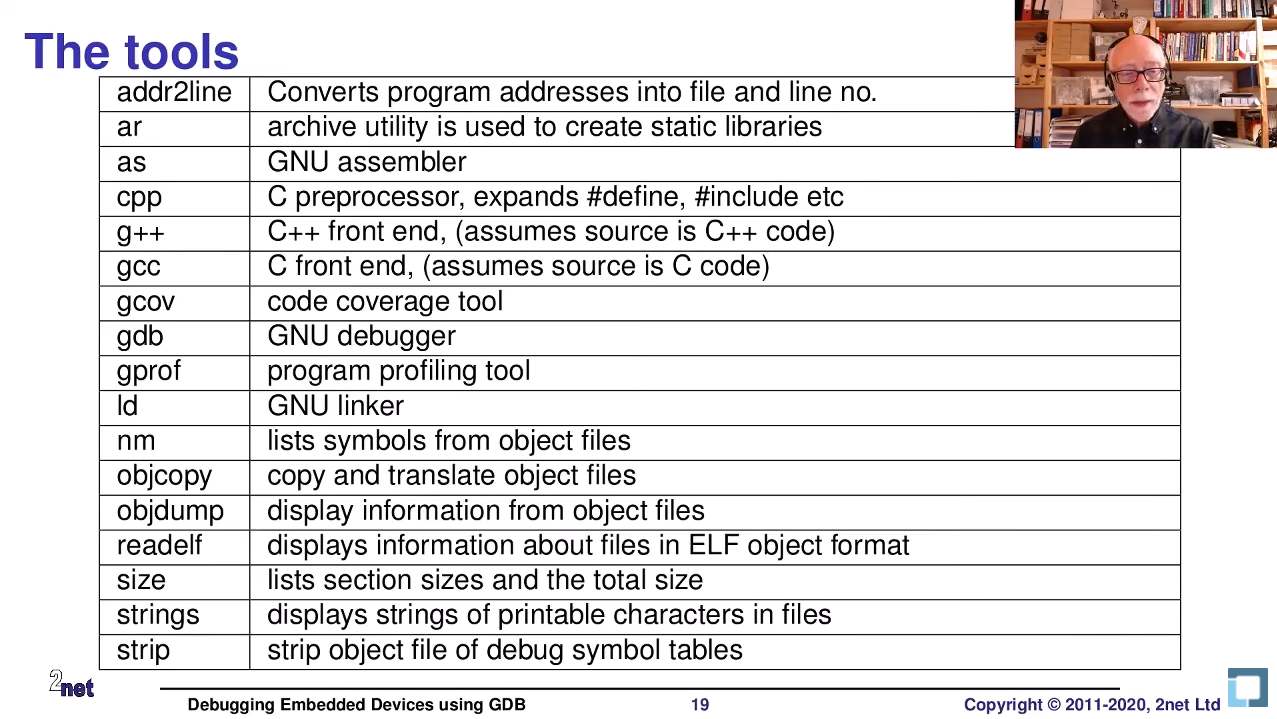 Ref: Linux Foundation 2020 Conference
Ref: Linux Foundation 2020 Conference
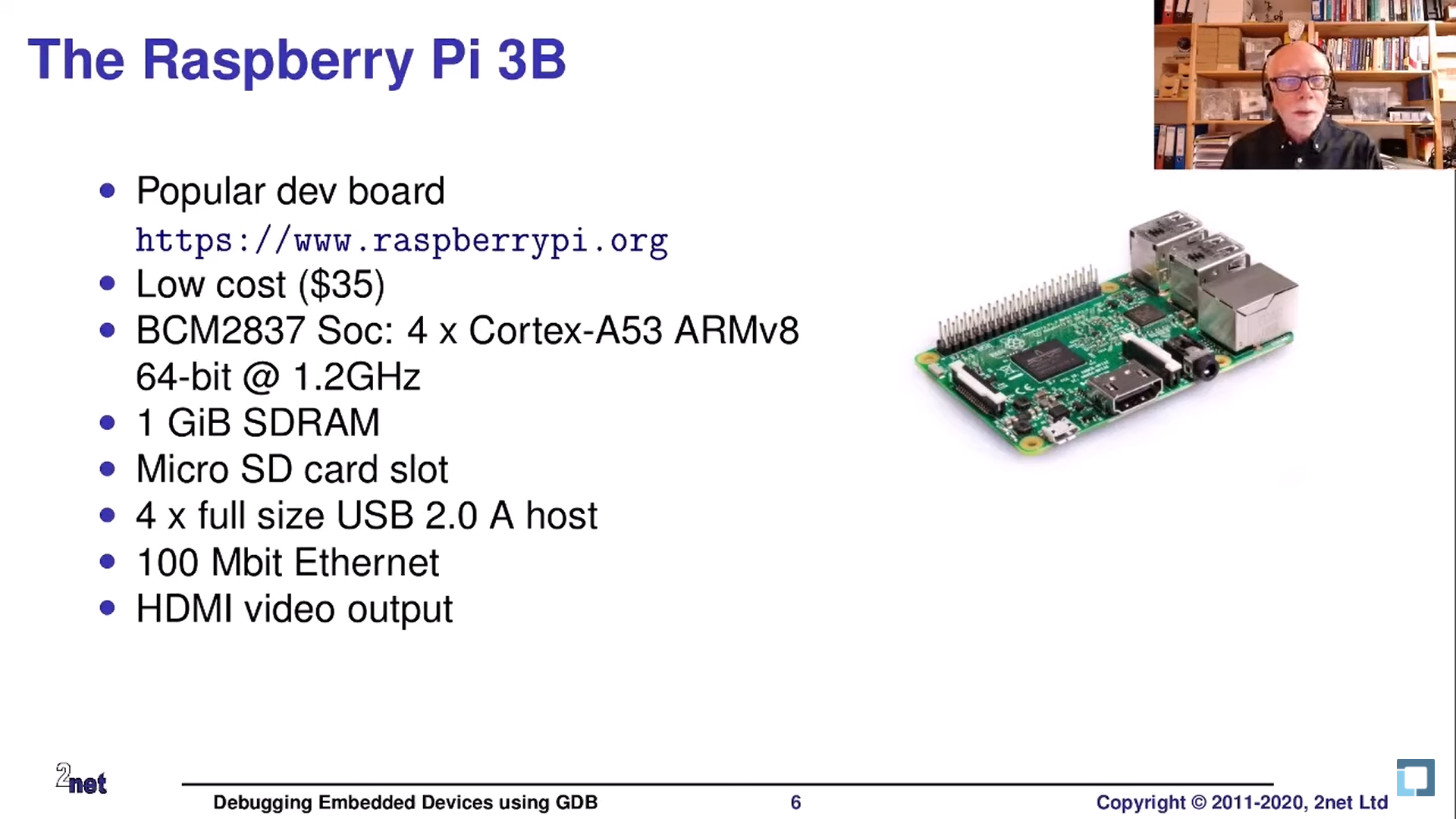
Example
라즈베리파이을 타겟으로 개발한다고 가정하자.
 Ref: Linux Foundation 2020 Conference
Ref: Linux Foundation 2020 Conference
요즘은 SBC(Single Board Computer)라고 불리울 만큼 10여년 전으로만 돌아가도 컴퓨터라고 불려도 무색할 성능이다. 하지만 임베디드기기는 임베디드기기 일뿐, 우리의 호스트 컴퓨터 성능에 미치지는 못할 뿐더러, 기기의 목표가 PC를 대체하는 것은 아니지 않은가? 이야기가 좀 샜다. ㅋㅋ;;
라즈베리파이 3B 모델의 Toolchain 은 공식적으로 아래 6개이다.
- arm-bcm2708hardfp-linux-gnueabi
- arm-bcm2708-linux-gnueabi
- arm-linux-gnueabihf
- arm-rpi-4.9.3-linux-gnueabihf
- gcc-linaro-arm-linux-gnueabihf-raspbian
- gcc-linaro-arm-linux-gnueabihf-raspbian-x64
자 이름에 공통점들이 보이는가?
이 순서를 보통 Triple 이라고 부르는데,
요즘은 <arch>-<vender>-<kernel>-<os> 이 기본 룰이고 그 앞뒤로 조금씩 바꿔서 사용하는 듯하다. (자세한 것 더 찾아봐야한다)